Content
1. Four Core Technologies of Roller Guide Shoes
Precision Bearing Design: Reduces Rolling Resistance
Double-Row Angular Contact Ball Bearings: Withstands Radial and Axial Loads, Ensuring High-Speed Roller Rotation without Binding
Preload Adjustment: A spring or hydraulic mechanism maintains constant contact between the roller and the guide rail, preventing bouncing.
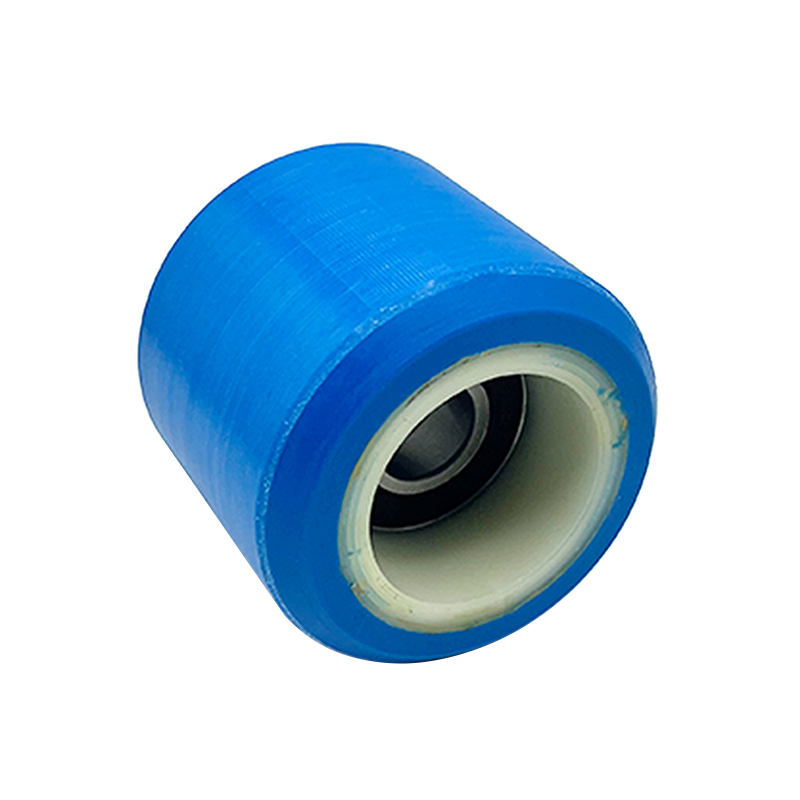
Polymer Material Rollers: Balances Shock Absorption and Wear Resistance
Polyurethane (PU) Rollers: Highly elastic and wear-resistant, absorbing micro-vibrations caused by guide rail unevenness.
Nylon Composite Rollers: Suitable for high-speed elevators (>2.5 m/s), with strong deformation resistance.
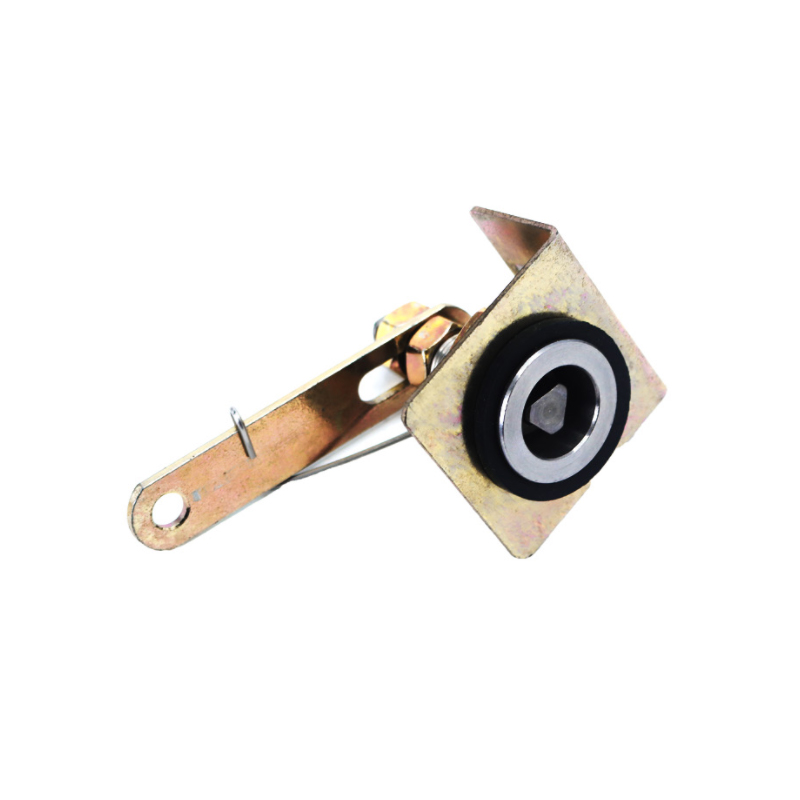
Dynamic Self-Aligning Structure: Accommodates Guide Rail Deflection
Floating Mounting: Allows the roller to adapt to guide rail installation errors within a ±3° range.
Elastic Support System: Rubber pads or springs cushion transient impact forces (such as during an emergency stop).
Lubrication Technology Innovation: Maintenance-Free and Long-Life
Self-lubricating bearings: Built with graphite or PTFE, no external lubrication is required.
Sealed design: Dust- and water-resistant, preventing impurities from entering the rollers and affecting performance.
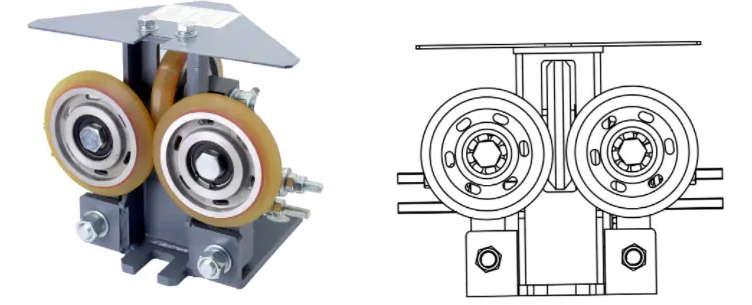
2. Common Elevator Roller Guide Shoe Problems and Solutions (Maintenance Guide)
Abnormal Roller Wear
- Uneven Roller Surface Wear
Possible Causes:
Guide Rail Installation Deviation (Horizontal/Vertical Tolerance Exceeded)
Car Unbalanced Loading Leading to Excessive Force on One Side
Unqualified Roller Material (Insufficient Hardness or Deterioration)
Solution:
Check Guide Rail Straightness: Use a laser alignment tool to ensure deviation is less than 0.5 mm/m.
Adjust Car Balance: Check the counterweight configuration to ensure even load distribution.
Replace High-Wear Rollers: Choose polyurethane (PU) or nylon composite materials (recommended Shore hardness 75A-85A).
- Premature roller cracking or deformation
Possible causes:
Overload (exceeding 150% of the rated load)
Excessively high ambient temperature (>60°C) causing softening of the PU roller
Chemical corrosion (such as strong acids or alkalis in cleaning agents)
Solution:
Install an overload protection device: Link the elevator control system to limit overload operation.
Replace high-temperature rollers: Choose nylon or PTFE composite materials (suitable for -30°C to 120°C).
Avoid chemical contact: Use a neutral solvent (such as alcohol) when cleaning.
Abnormal Operational Noise
- A "creaking" sound during rolling
Possible causes:
Lack of bearing oil or dust intrusion
Worn roller pin causing increased clearance
Hard particles (such as sand and gravel) on the guide rail surface
Solution:
Clean and lubricate the bearings: Use high-temperature grease (such as lithium-based grease). Sealed bearings should be replaced immediately.
Replacing the pin: Check the pin diameter for wear (>0.2mm requires replacement). Clean the guide rails: Use fine sandpaper to polish the guide rail contact surface to remove impurities.
- High-frequency "buzzing" vibration
Possible causes:
Failure of roller dynamic balancing (e.g., internal bearing damage)
Resonance between the elevator's operating speed and the roller's natural frequency
Solution:
Replace the roller assembly: Prefer genuine parts (dynamic balancing accuracy ≤ 0.5g·cm).
Adjust the elevator's operating curve: Use the inverter to reduce acceleration and avoid the resonant frequency band.
Guide shoe jamming
- Sluggish roller rotation
Possible causes:
Bearing corrosion (caused by a humid environment)
Insufficient clearance between the roller and the guide rail (improper installation)
Solution:
Replace stainless steel bearings: Suitable for high-humidity environments (e.g., elevators in underground garages).
Adjust the guide shoe clearance: Use a feeler gauge to measure; a clearance of 0.5-1mm per side is recommended (refer to manufacturer's standards).
Other Systemic Failures
- The guide shoe is completely deflected or loose.
Possible Causes:
Loose mounting bolts (due to vibration)
Deformed guide shoe bracket (due to external impact)
Solution:
Tighten the bolts and apply anti-loosening seal: Use a torque wrench (tighten to the manufacturer's specified torque).
Align or replace the bracket: Use a level to check the bracket flatness (error <1mm/m).
3. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ) about Elevator Roller Guide Shoes
- How do I determine if a roller needs replacement?
Replacement criteria:
Wear: Roller diameter reduction > 2mm (measured with a caliper).
Surface cracks: Visible cracking or peeling.
Abnormal noise/vibration: Noticeable creaking or shaking during operation.
- Do roller guide shoes require lubrication?
Most do not:
Modern roller guide shoes use self-lubricating bearings (such as graphite-filled PTFE).
Exceptions: Older models or special environments (high temperatures) may require a small amount of high-temperature grease.
- Why do rollers wear prematurely?
Common causes:
Guide rail installation deviation (> 1mm/m).
Chronic unbalanced car loading (e.g., heavy objects are always placed on one side).
Using low-quality rollers (hardness does not meet the standard).
- Are roller guide shoes suitable for high-speed elevators? Applicability:
Low-speed elevators (≤1.75 m/s): Ordinary PU rollers are sufficient.
High-speed elevators (≥2.5 m/s): Nylon composite rollers with precision bearings are required.
- How can I reduce the noise of roller guide shoes?
Noise reduction measures:
Select guide shoe brackets with elastic pads (vibration-absorbing design).
Ensure smooth guide rail joints (polish the transition area).
Replace silent bearings.


 English
English 中文简体
中文简体











