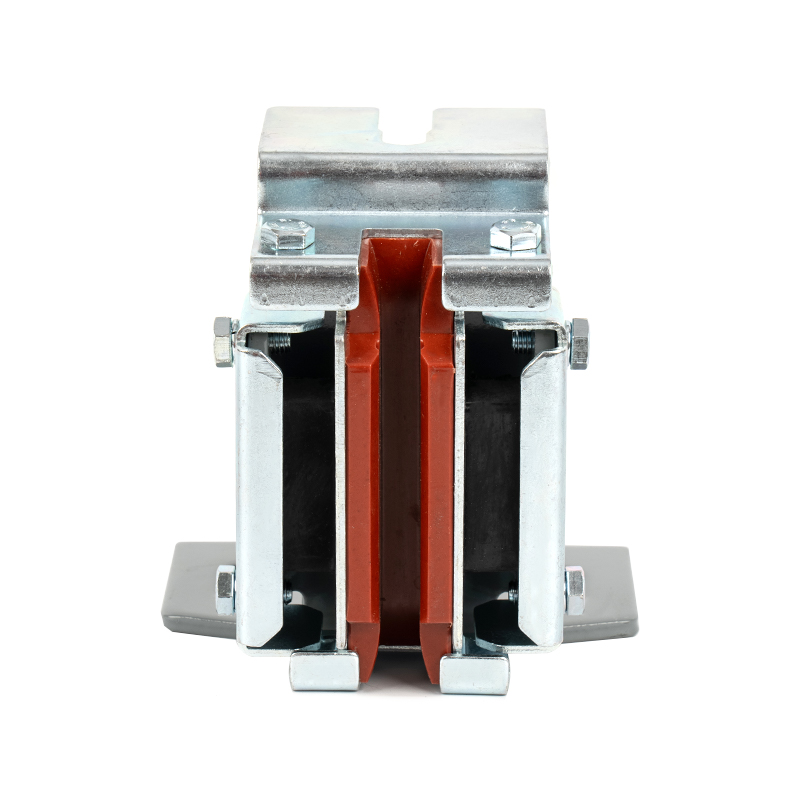
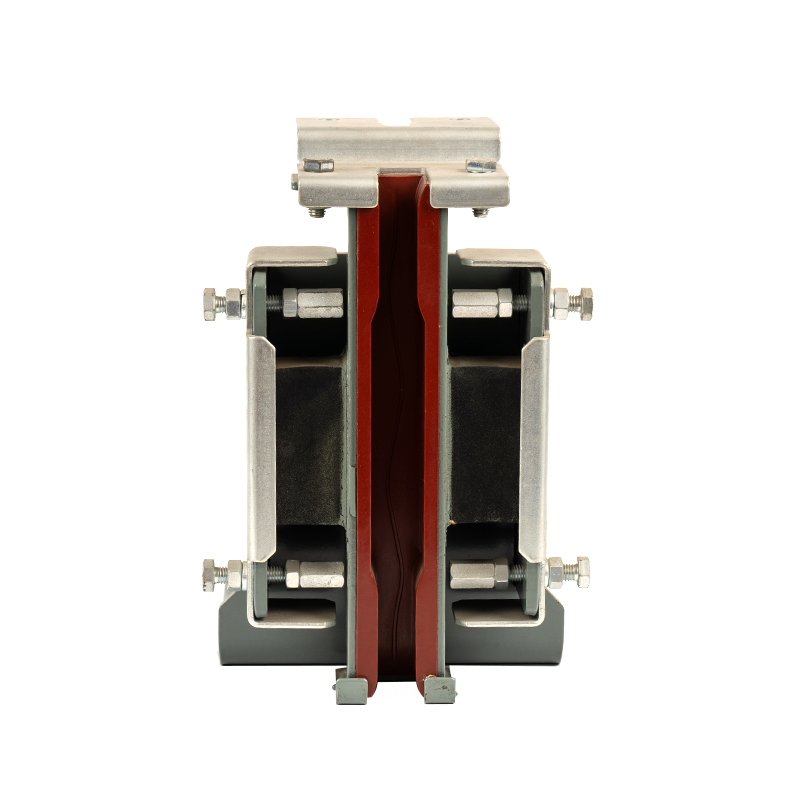
Elevator guide shoes (commonly called guide shoes) are crucial safety guide components in elevator systems, primarily installed on both sides of the elevator car and counterweight. The guide shoe consists of a shoe head, a shoe body, and a shoe seat. The shoe head provides guidance and support, the shoe body transmits force and torque, and the shoe seat secures the guide shoe to the equipment chassis. Sliding guide shoes are widely used in transportation equipment such as elevators and high-speed trains. Their functions are reflected in the following aspects:
Content
1. Guidance and Stable Operation
Core Function: The guide shoe adheres to and "rides" on the elevator guide rails, much like a train wheel on a track.
Sway Limitation: Ensures that the elevator car and counterweight move along fixed vertical tracks during up and down travel, preventing the car/counterweight from swaying, rocking, or twisting horizontally (forward, backward, left, and right).
Stableness: A key component for smooth elevator operation and passenger comfort. Without effective guidance from the guide shoe, the elevator will experience severe vibration and noise.
2. Reducing Vibration and Noise:
The contact surface between the guide shoe (especially the elastic guide shoe) and the guide rail is typically equipped with a pad or slider made of a wear-resistant material (such as nylon or polyurethane).
These materials have a certain degree of elasticity and shock absorption properties, which can absorb some of the vibration generated during operation and convert the hard friction between metals into relatively gentle sliding friction, thereby significantly reducing operating noise.
3. Withstanding Horizontal Forces:
Horizontal forces are generated during elevator starting, braking, acceleration and deceleration, and when passengers enter and exit the elevator car, causing load shifts.
The guide shoe transmits these horizontal forces to the sturdy elevator guide rail, which ultimately transmits them to the elevator shaft structure, preventing these forces from deforming the car structure or affecting operational safety.
4. Preventing Rail Gnawing and Derailment:
Effective guide action prevents the car or counterweight from colliding with the guide rail (known as "rail gnawing"), thus avoiding excessive wear on the guide rail and guide shoe.
More importantly, it prevents the most dangerous situation: the car or counterweight derailing from the guide rail, which is an extremely serious safety accident.
5. Types and Applicability:
Fixed Sliding Guide Shoes: These have a simple structure and low cost, but they also have high friction resistance and relatively noticeable noise and vibration. They are primarily used in low-speed, low-load elevators (such as freight elevators).
Elastic Sliding Guide Shoes: These are the most common type. They contain elastic elements such as springs or rubber, allowing the liner to adapt to even minor unevenness or deflection in the guide rail, maintaining constant contact pressure. This reduces friction and results in smoother and quieter operation. They are widely used in low- and medium-speed passenger elevators.
Roller Guide Shoes: These use rollers instead of sliding liner, resulting in minimal friction resistance and extremely smooth and quiet operation. However, their structure is complex and costly, and they are primarily used in high- and ultra-high-speed elevators.
In summary, the core functions of elevator guide shoes are:
Guidance: Ensures that the car and counterweight run strictly along the vertical guide rails, without shaking or swaying.
Stability: Maintains smooth operation and enhances ride comfort.
Vibration and Noise Reduction: The elastic material and structure absorb vibration and reduce friction noise. Force Transmission: Withstands and transmits various horizontal forces during operation, protecting the car structure and hoistway.
Safety: Prevents rail gnawing and derailment, ensuring safe elevator operation.


 English
English 中文简体
中文简体